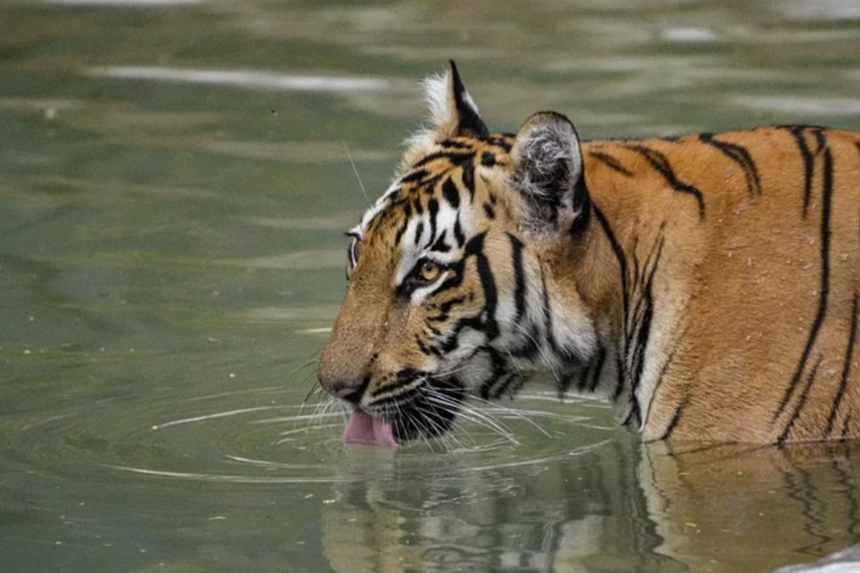
Every year on July 29, the world observes International Tiger Day to raise awareness about tiger conservation and celebrate efforts to protect this iconic species. The day was established at the 2010 Saint Petersburg Tiger Summit, where 13 tiger-range countries pledged to double the global wild tiger population by 2022 under the “Tx2” initiative. While some countries are still working toward this goal, India has made remarkable progress—now home to over 3,600 tigers, accounting for nearly 75% of the world’s wild tiger population.
Tigers play a crucial role in maintaining healthy forest ecosystems as apex predators. Their presence helps balance prey populations, which in turn supports vegetation and overall biodiversity. Despite their ecological importance, tigers face ongoing threats including habitat loss, poaching, and human-wildlife conflict. Conservation strategies—such as India’s Project Tiger and the use of monitoring tools like M-Stripes—have been essential in tracking tiger populations and enhancing protection efforts across reserves.
International Tiger Day is an opportunity to renew global commitment to conservation. Schools, communities, and conservation groups commemorate the day with awareness campaigns, educational programs, and fundraising for tiger protection. As climate pressures and human development continue to shrink tiger habitats, it’s more important than ever to support policies and practices that ensure these big cats can thrive for generations to come.
Due to concerns including poaching, habitat destruction, and human conflict, the tigers, which were formerly widely distributed throughout Asia, now only exist in a small number of reserves.
 unknownx500
unknownx500